Obesity Surgery
Obesity surgery, also known as bariatric surgery, is a transformative procedure for individuals struggling with severe obesity. This surgery aims to aid significant weight loss and improve overall health by altering the digestive system. This comprehensive guide will cover various aspects of obesity surgery, from preparation to recovery, highlighting its benefits and answering common questions.
What is Obesity Surgery?
Obesity surgery encompasses various procedures designed to help patients lose weight by making changes to their digestive system. The most common types include gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, and adjustable gastric banding. Each procedure works differently but shares the goal of reducing the amount of food the stomach can hold, thereby promoting weight loss.
Who is a Candidate for Obesity Surgery?
Not everyone is a suitable candidate for obesity surgery. Generally, candidates are individuals with a body mass index (BMI) of 40 or higher, or a BMI of 35 or higher with serious obesity-related health conditions like diabetes, hypertension, or sleep apnea. Additionally, candidates must demonstrate a history of unsuccessful weight loss attempts through diet and exercise.

Preparing for Obesity Surgery
Preparing for obesity surgery involves several crucial steps. Patients typically undergo comprehensive medical evaluations, nutritional counseling, and psychological assessments to ensure they are ready for the procedure. Preoperative preparation often includes following a specific diet to reduce liver size and minimize surgical risks. Proper preparation is key to a successful surgery and recovery.
Types of Obesity Surgery
Gastric Bypass
Gastric bypass is one of the most common types of obesity surgery. It involves creating a small pouch at the top of the stomach and connecting it directly to the small intestine. This bypasses most of the stomach and part of the intestines, significantly reducing calorie absorption.
Sleeve Gastrectomy
Sleeve gastrectomy involves removing approximately 80% of the stomach, leaving a tube-like structure. This smaller stomach limits the amount of food that can be consumed and reduces the production of ghrelin, the hormone responsible for hunger.
Adjustable Gastric Banding
Adjustable gastric banding, often known as the lap band, involves placing a band around the upper part of the stomach to create a small pouch. The band can be adjusted to control the size of the opening to the rest of the stomach, regulating food intake.
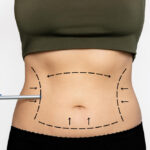
The Surgical Procedure
The obesity surgery procedure typically requires general anesthesia and can be performed laparoscopically, involving small incisions and a camera to guide the surgery. This minimally invasive approach reduces recovery time and the risk of complications. The specific details of the surgery will depend on the type of procedure chosen.
Recovery and Aftercare
Recovery from obesity surgery varies depending on the individual and the type of procedure. Generally, patients stay in the hospital for a few days and may take several weeks to return to normal activities. Postoperative care includes a specific diet progression, starting with liquids and gradually moving to solid foods. Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor progress and address any issues.

Benefits of Obesity Surgery
The benefits of obesity surgery extend beyond significant weight loss. Patients often experience improvements in obesity-related conditions such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and sleep apnea. Additionally, weight loss can lead to increased mobility, improved mental health, and a better quality of life. The transformative potential of obesity surgery makes it a valuable option for individuals struggling with severe obesity.
Conclusion
Understanding obesity surgery involves exploring its various aspects, from candidate evaluation and preparation to the surgical procedure and recovery. The benefits of this surgery can be life-changing, improving not only physical health but also mental well-being and overall quality of life. By thoroughly understanding the process and potential outcomes, individuals can make informed decisions about their health and weight loss journey.
FAQ
- What is obesity surgery?
- Obesity surgery, also known as bariatric surgery, involves procedures that alter the digestive system to promote weight loss.
- Who qualifies for obesity surgery?
- Candidates typically have a BMI of 40 or higher, or 35 or higher with obesity-related health conditions, and have not succeeded with other weight loss methods.
- What are the types of obesity surgery?
- The main types are gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, and adjustable gastric banding.
- How do I prepare for obesity surgery?
- Preparation includes medical evaluations, nutritional counseling, psychological assessments, and following a pre-surgery diet.
- What is the recovery time for obesity surgery?
- Recovery generally takes several weeks, with specific dietary guidelines to follow and regular follow-up appointments.
- What are the risks of obesity surgery?
- Risks include infection, blood clots, and nutritional deficiencies. Long-term complications may involve gastrointestinal issues.
- How much weight can I expect to lose after obesity surgery?
- Weight loss varies, but patients can expect to lose 50-70% of their excess weight within the first two years.
- Will obesity surgery cure my diabetes?
- Many patients experience significant improvements or remission of type 2 diabetes following obesity surgery.
- Can I have children after obesity surgery?
- Yes, but it’s recommended to wait at least 12-18 months post-surgery to ensure your body is healthy and stable.
- What are the long-term benefits of obesity surgery?
- Long-term benefits include sustained weight loss, improved overall health, increased mobility, and enhanced quality of life.